Organic Molecules Mrs. CovarrubiasAdvanced Biology
Chapt01+Fig+Cont+ZCD1. 1: Organic Molecules and Chemical Bonding. Preview 1-3. 1.1 Organic Molecules 1-4. Bonding Characteristics of Atoms. (1.1A) 1-4. Bonds and Unshared Electron Pairs for C, N, O, and F. Bonds and Unshared Electron Pairs for Other Atoms. Structures of Organic Molecules.

Organic Chemistry 101 Nomenclature Organic chemistry reactions
Organic chemistry 14 units. Unit 1 Structure and bonding. Unit 2 Resonance and acid-base chemistry. Unit 3 Alkanes, cycloalkanes, and functional groups. Unit 4 Stereochemistry. Unit 5 Substitution and elimination reactions. Unit 6 Alkenes and alkynes. Unit 7 Alcohols, ethers, epoxides, sulfides. Unit 8 Conjugated systems and pericyclic reactions.

Organic Molecules Chart
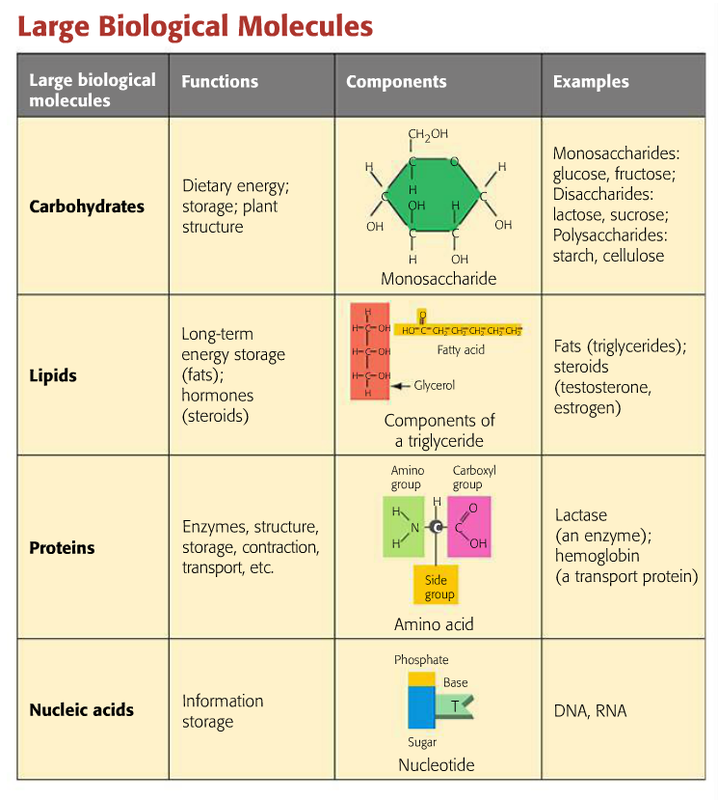
Meaning. A large, organic molecule such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. A molecule that is a building block for larger molecules (polymers). For example, an amino acid acts as the building blocks for proteins. A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers).

The table shows the energy that is stored in three types of organic
Tim Soderberg. University of Minnesota Morris. An understanding of the various types of noncovalent forces allows us to explain, on a molecular level, many observable physical properties of organic compounds. In this section, we will concentrate on solubility (especially solubility in water), melting point, and boiling point.

Probable chemical mechanisms of different classes of organic compounds
The chemistry of these compounds is called organic chemistry. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen. The alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons—that is, hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds. Alkenes contain one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkynes contain one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds.

CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Introduction. In its simplest definition, organic compounds include all molecules that contain carbon. By this definition, simple molecules such as carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) would be defined as organic molecules, however, these simple molecules behave more like inorganic molecules than organic molecules.

😂 Which is an organic molecule. CHEMISTRY II WATER AND ORGANIC
Substitutive nomenclature is the main method for naming organic-chemical compounds. It is used mainly for compounds of carbon and elements of Groups 13-17. For naming purposes, a chemical compound is treated as a combination of a parent compound (Section 5) and characteristic (functional) groups, one of which is
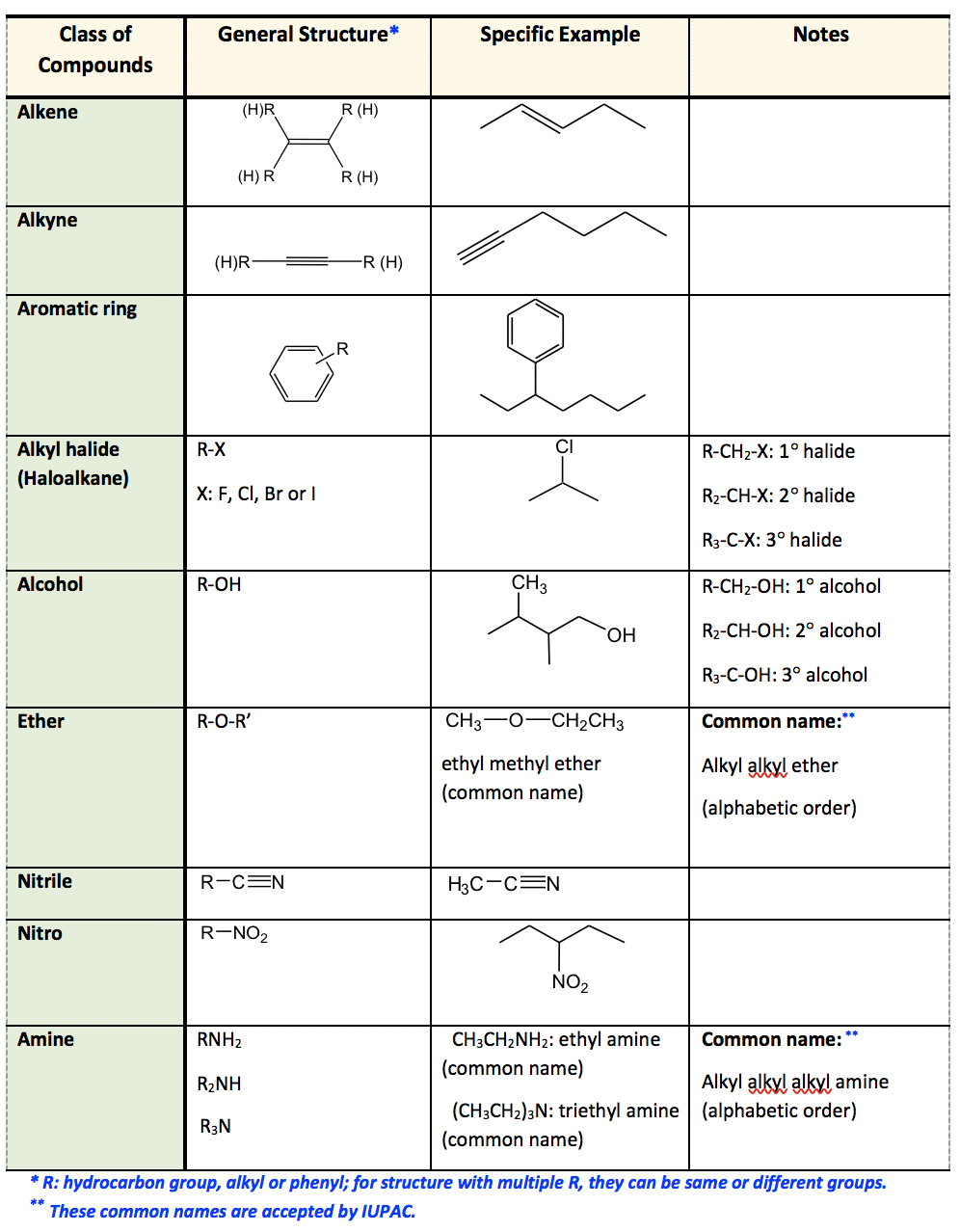
2.3 Functional Groups Organic Chemistry I
The purpose of this chart will be clear if you've got a background in chemistry. If you haven't, it's a useful tool to decode the different parts that make up molecules in organic chemistry. All carbon-based (organic) molecules contain functional groups - some more than one of them - and they're what gives molecules their particular.
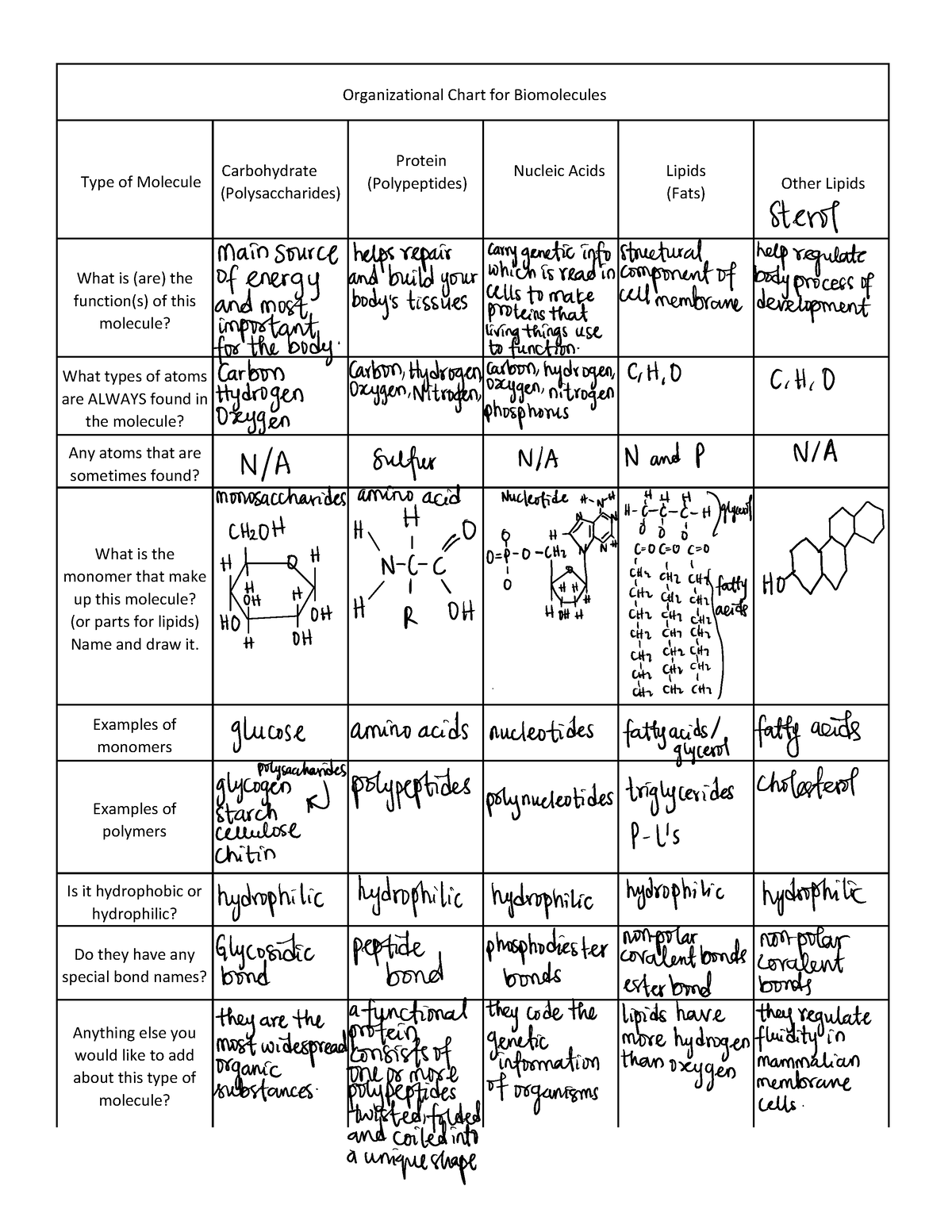
Organic Molecules worksheet Organizational Chart for Biomolecules
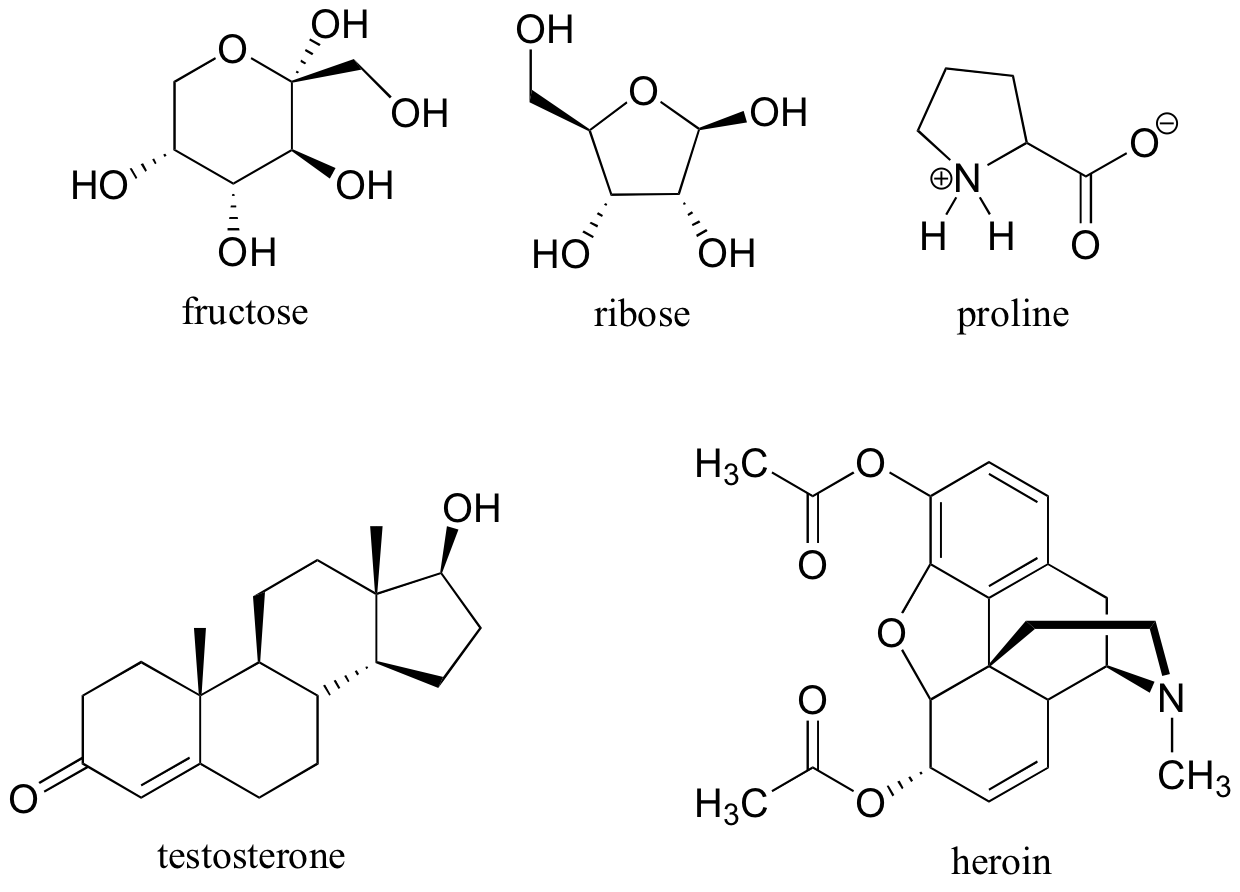
The structures, abbreviations (both three- and one-letter), and pK a values of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins are shown in Table 26.1.All are α-amino acids, meaning that the amino group in each is a substituent on the α carbon—the one next to the carbonyl group. Nineteen of the twenty amino acids are primary amines, RNH 2, and differ only in the nature of their side chain.

Organic Molecules Chart Organic Molecules Contrast Chart school
Figure 26.1. 2: The Tetrahedral Methane Molecule. Methane (CH 4 ), ethane (C 2 H 6 ), and propane (C 3 H 8) are the beginning of a series of compounds in which any two members in a sequence differ by one carbon atom and two hydrogen atoms—namely, a CH 2 unit. The first 10 members of this series are given in Table 26.1.

Organic functional groups chart expanded edition M A N O X B L O G
For many purposes, ball-and-stick models of organic compounds give useful information about the spatial relationships of the atoms, and for \(CX_4\) the angles between sticks are set at \(109.5^\text{o}\) (Figure 2-1). Organic molecules strongly resist deformation forces that alter their valence angles from normal values.

chemistry nomenclature Organic chemistry, Chemistry education
Table 2.4 Subordinate Groups. We will go through several examples for more details about the naming rules. 1. The parent structure is the 6-carbon carboxylic acid with a double bond, so the last name comes from "hexene". To add the suffix, the last letter "e" will be dropped, so the parent name is "hexeneoicacid".

PPT Organic Molecules and Carbohydrates PowerPoint Presentation, free
CH 3 (CH 2) 8 CH 3. 174. kerosene. Alkanes with four or more carbon atoms can have more than one arrangement of atoms. The carbon atoms can form a single unbranched chain, or the primary chain of carbon atoms can have one or more shorter chains that form branches. For example, butane (C 4 H 10) has two possible structures.

2.3 Biologically Important Macromolecules Biology LibreTexts
Drawing the Structure of Organic Molecules. Although larger molecules may look complicated, they can be easily understood by breaking them down and looking at their smaller components. All atoms want to have their valence shell full, a "closed shell." Hydrogen wants to have 2 e - whereas carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen want to have 8 e -.
3.2 Conformations of cyclic organic molecules Chemistry LibreTexts
1. Organic compounds containing substituents from Group C are named following this sequence of steps, as indicated on the examples below: •Step 1. Find the longest continuous carbon chain. Determine the root name for this parent chain. In cyclic compounds, the ring is usually considered the parent chain, unless it is
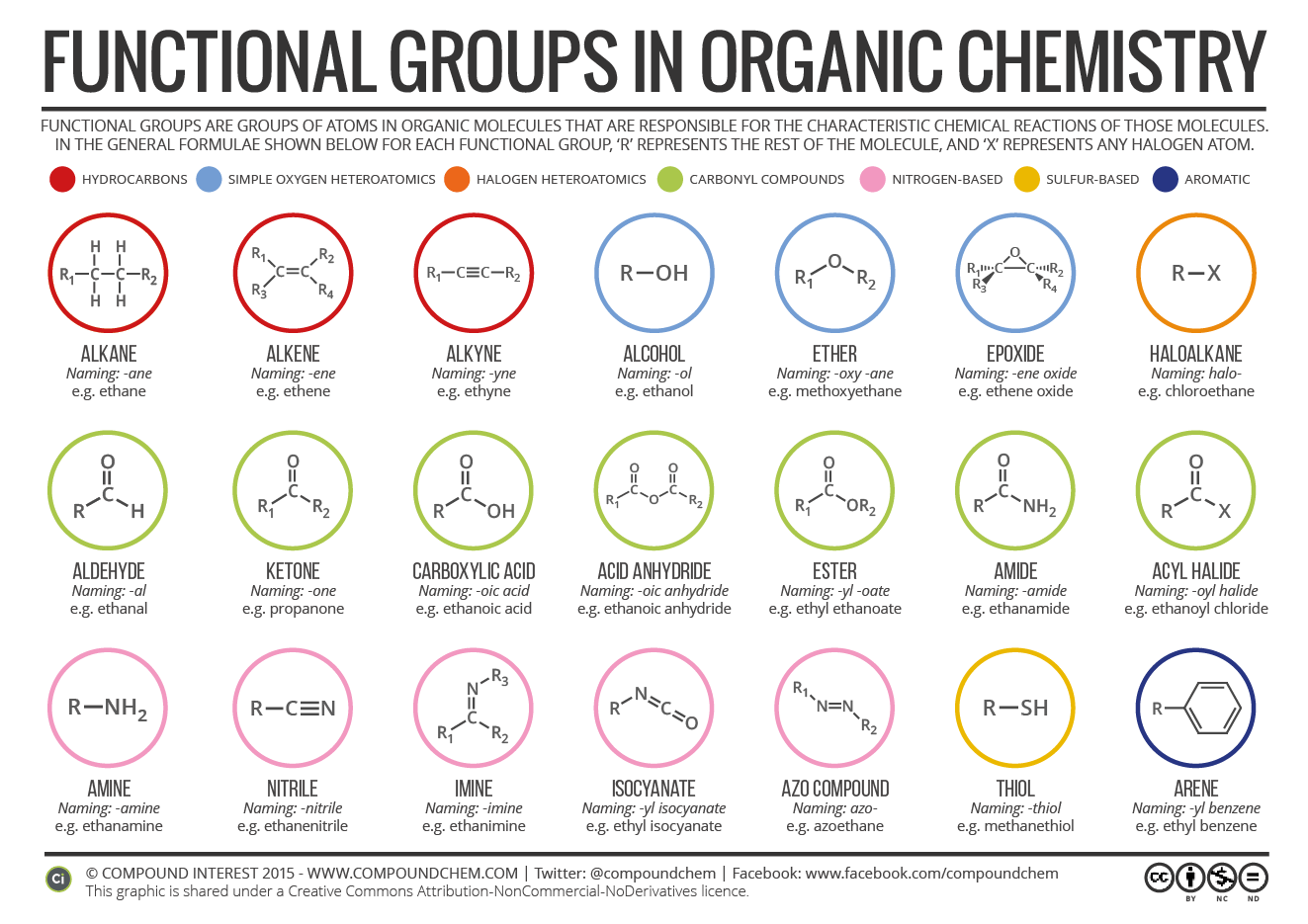
Functional Groups in Organic Compounds
They are small, simple compounds that play important roles in the cell, although they do not form cell structures. Most of the carbon found in organic molecules originates from inorganic carbon sources such as carbon dioxide captured via carbon fixation by microorganisms. Exercise 7.1.2 7.1. 2. Describe the most abundant elements in nature.